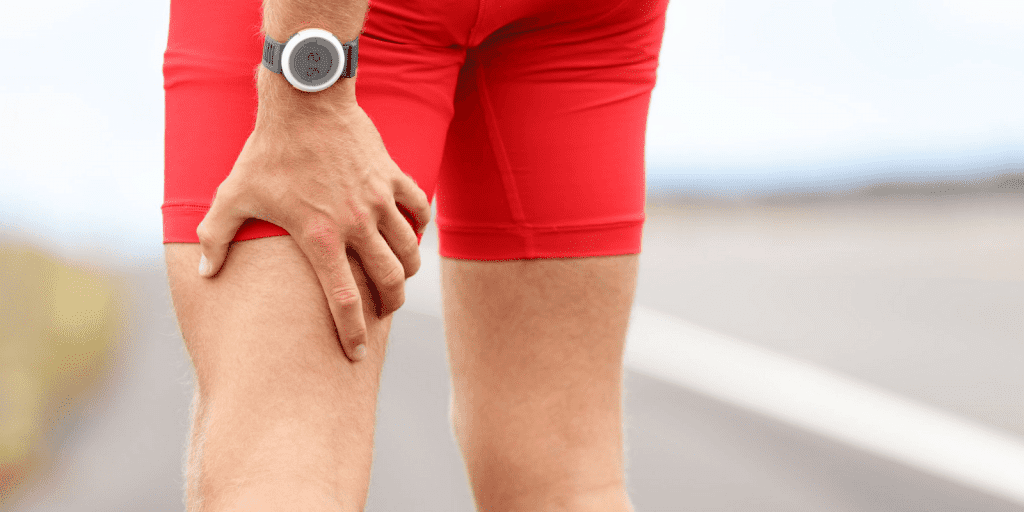
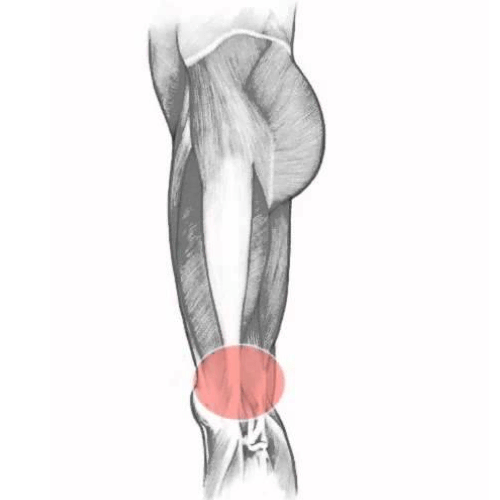

Hamstring strains are one of the most common musculoskeletal injuries seen in active populations and make up 92% of muscular strains in soccer.1 Sports including track and field, soccer and weight lifting have been found to have high recurrence rates with respect to this injury. 2
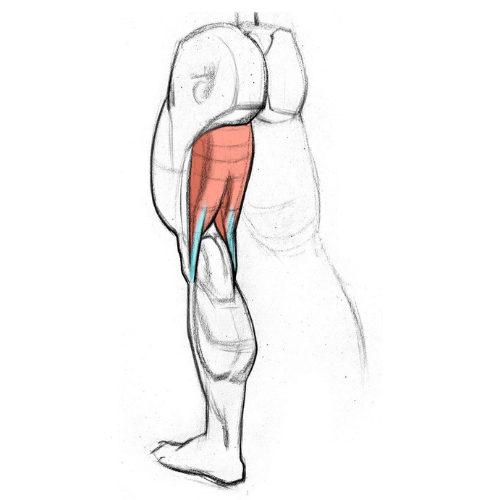
The hamstring complex comprises three muscles in the back of your thigh. Starting from the inner part of your thigh and moving outwards, they are: semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris. Any of these three muscles can become injured during activity.
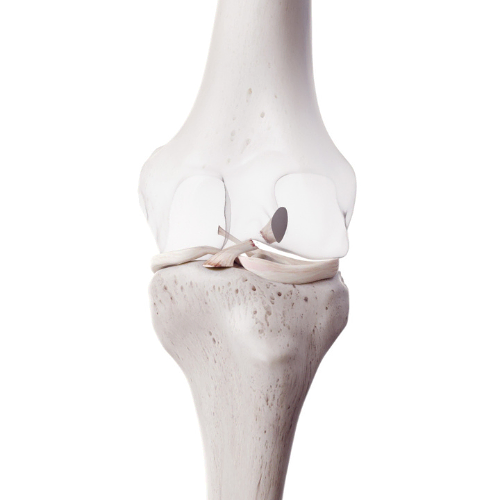
The hamstring muscles originate at the bottom of the pelvis and attach into the shin bones just below the knee. They are responsible for bending (flexion) at the knee and straightening (extending) the hip.3 When the hamstring complex is placed under a forceful load, this puts individuals at an increased risk for strains and ruptures. Studies indicate that a hamstring injury occurs most often during the late swing phase of sprinting, followed by eccentric loading (where the muscle is lengthening under load).3-4
Muscular imbalances can also play a key role in hamstring injuries. For example the quadricep muscles are typically 20-30% stronger than the hamstring complex and imbalance between the two muscle groups can be problematic. Muscular weakness and improper firing patterns between the glutes and hamstring muscles are also very common amongst a wide range of people. Lastly, improper warm up prior to taking part in activities and sport puts one at a higher risk of sustaining a hamstring injury.3
Muscle strains can be separated into three categories based on the extent of damage to the tissues- Grades I, II, III.3
A registered physiotherapist or chiropractor can assess to aid in diagnosing a hamstring injury. This includes a detailed history of how the injury occurred, and a hands-on assessment to look at the muscle length, strength, and function. Typically, a referral for imaging, such as an ultrasound, is not necessary unless there is a suspected complete rupture. If this is the case, a consultation with a physician may be appropriate to be referred for imaging.
Muscle strains are one of the most common causes of time missed due to injury in a variety of sports.6 It is important to understand that recovery time will be different for every individual. Factors including mechanism of injury, degree of damage, age, training levels, and past medical history can affect the length of recovery. Studies show that athletes sustaining a hamstring injury in elite sports such as rugby and football will most likely undergo a longer recovery period.7 Moreover, if you’re an athlete who participates in sports regularly, your muscles are working even harder under forceful loads than the average person.
Tissue healing time is classified into three different phases: 9-10
Inflammation – The inflammatory response phase typically occurs immediately following an injury and could last up to four days. Signs and symptoms of inflammation can include redness, associated pain, swelling, and warmth or heat to the touch. The ultimate goal of the inflammatory phase is to prevent further blood loss at the lesion site. Moreover, this response causes blood vessels to constrict (vasoconstriction) which results in a blood clot or scab.
Proliferation – Proliferation is the second phase of healing which begins around the fourth day post-injury and could last up to twenty-one days depending on various factors. The key purpose of this phase is to clear the injury site of any debris. Cells will aid in developing new blood vessels and laying down connective tissue.
Remodeling – The remodeling phase is the final phase of healing that begins approximately twenty-one days post-injury and could last up to two years. The main purpose of this phase is for cells to overlap new tissue, joining the edges of the wound together. Collagen fibers are re-organized and scar tissue formation begins.